Wildfires: How to cope when smoke affects air quality and health

What can magnesium do for you and how much do you need?

Dry socket: Preventing and treating a painful condition that can occur after tooth extraction

What happens during sleep �� and how to improve it

How is metastatic prostate cancer detected and treated in men over 70?

Could biofeedback help your migraines?

What is autism spectrum disorder?

Plantar warts: Options for treating this common foot condition

Cancer survivorship: What comes next after treatment

Nutritional yeast: Does this savory, vegan seasoning pack a nutritional punch?
Cancer Archive
Articles
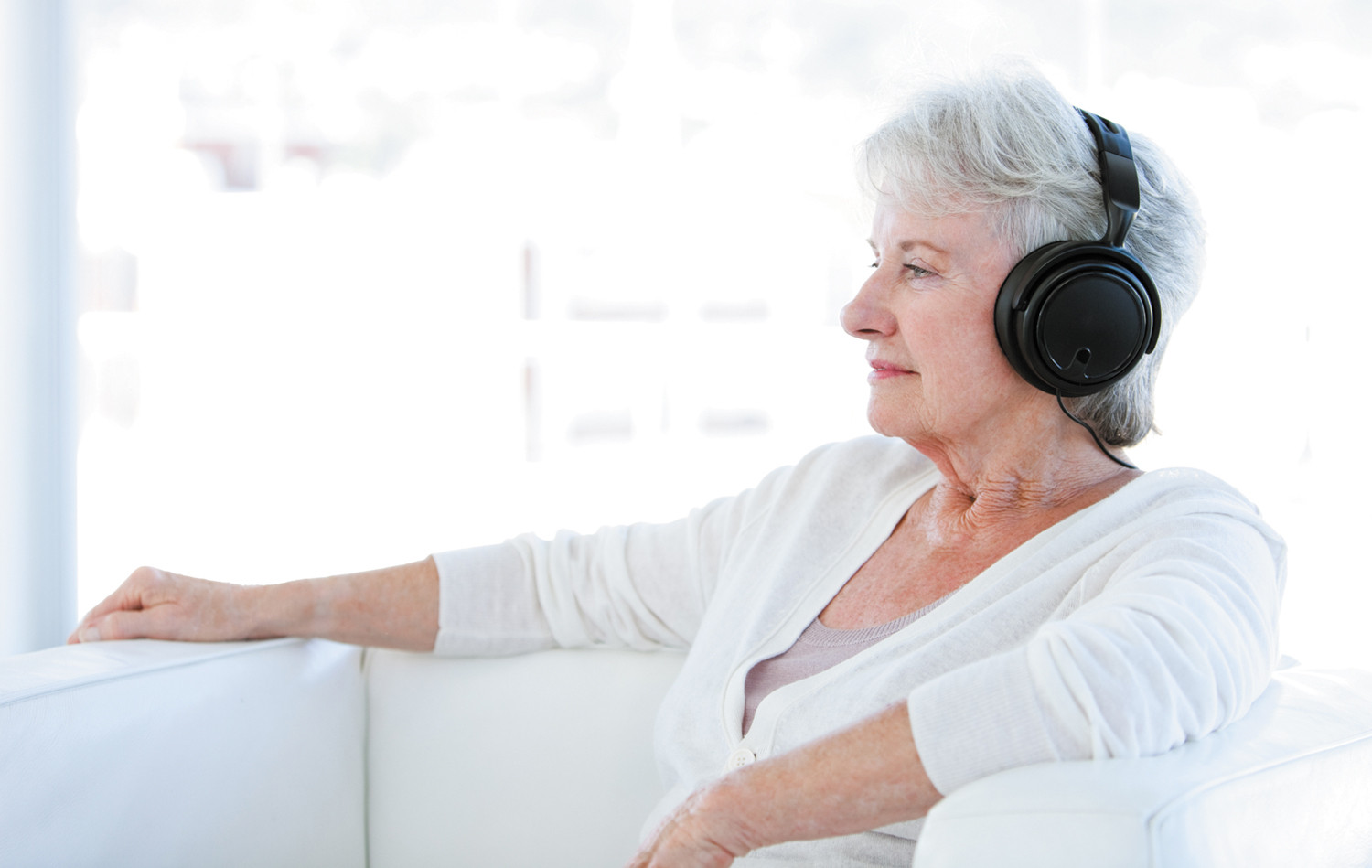
How music can help you heal
Music therapy can calm anxiety, ease pain, and provide a pleasant diversion during chemotherapy or a hospital stay.
It's almost impossible to find someone who doesn't feel a strong connection to music. Even if you can't carry a tune or play an instrument, you can probably reel off a list of songs that evoke happy memories and raise your spirits. Surgeons have long played their favorite music to relieve stress in the operating room, and extending music to patients has been linked to improved surgical outcomes. In the past few decades, music therapy has played an increasing role in all facets of healing.
What is music therapy?
Music therapy is a burgeoning field. People who become certified music therapists are usually accomplished musicians who have deep knowledge of how music can evoke emotional responses to relax or stimulate people or help them heal. They combine this knowledge with their familiarity with a wide variety of musical styles to find the specific kind that can get you through a challenging physical rehab session or guide you into meditation. And they can find that music in your favorite genre, be it electropop or grand opera.
The empowering potential of end-of-life care
There’s almost always something we can do to improve our health and well-being �� even at the end of our lives. Palliative care is designed to improve the quality of life for people with life-threatening illnesses and their families by keeping a person comfortable and making sure his or her values and preferences guide the medical team’s actions. For this reason, good communication with your care team �� and your loved ones �� is essential, even before you or a loved one has developed a serious illness.
Taking new aim at cancer
Last year, only months after announcing that he had an aggressive form of melanoma, former President Carter declared that he was cancer free �� thanks at least in part to a recently approved immunotherapy drug. Immunotherapy is a type of targeted therapy that helps boost the body’s own immune response to cancer. It does so while sparing healthy cells, thus minimizing side effects.
Taking aim at cancer
Image: Thinkstock
Targeted cancer therapies have limits, but some may offer a better option than standard chemotherapy.
Mention cancer treatment, and most men think of chemotherapy—complete with hair loss and extreme fatigue. But for some men, there is another option. Targeted therapies can sometimes treat certain cancers with fewer side effects and better outcomes.
Some prostate cancer treatments increase heart attack risk
In the journals
If you have suffered a heart attack and plan to undergo prostate cancer treatment, you may want to weigh the risks and benefits of androgen deprivation therapy (ADT). ADT decreases the amount of androgens in the body, which prostate cancer needs to grow and survive. It is also often used along with radiation therapy, and the combination has been shown to prolong survival in men with unfavorable-risk prostate cancer—defined as cancer with two or more high-risk factors, like a PSA level between 10 and 40 ng/mL, a Gleason score of 7 or higher, or biopsies with 50% or higher cancerous cells.
But a study in The Journal of the American Medical Association suggests that men who had a prior heart attack can increase their risk of a fatal one if they undergo both radiation therapy and ADT. Researchers compared overall survival and death from prostate cancer, fatal heart attack, and other causes in a group of 206 men with unfavorable-risk prostate cancer. The men received either radiation alone, or radiation and six months of ADT. The researchers also categorized the men into subgroups based on other health conditions, including heart disease.
Colon cancer testing: What's in it for you?
Image: iStock
Being checked for hidden colorectal cancer is a smart bet, though it's hard to say whether it will ultimately extend your life span.
Recently, the National Colorectal Cancer Roundtable—a national organization of medical groups, health care providers, government agencies, and patient advocates—launched the "80% by 2018" initiative. The goal is to convince more people to get screened for hidden colorectal cancer. Right now, about 65% of Americans do so.

Wildfires: How to cope when smoke affects air quality and health

What can magnesium do for you and how much do you need?

Dry socket: Preventing and treating a painful condition that can occur after tooth extraction

What happens during sleep �� and how to improve it

How is metastatic prostate cancer detected and treated in men over 70?

Could biofeedback help your migraines?

What is autism spectrum disorder?

Plantar warts: Options for treating this common foot condition

Cancer survivorship: What comes next after treatment

Nutritional yeast: Does this savory, vegan seasoning pack a nutritional punch?
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up