Tips to leverage neuroplasticity to maintain cognitive fitness as you age

Can white noise really help you sleep better?

Celiac disease: Exploring four myths

What is prostatitis and how is it treated?

What is Cushing syndrome?

Exercises to relieve joint pain

Think your child has ADHD? What your pediatrician can do

Foam roller: Could you benefit from this massage tool?

Stepping up activity if winter slowed you down

Common causes of cloudy urine
Cancer Archive
Articles
E-cigarettes: Good news, bad news
While e-cigarettes do not produce the tar or toxic gases found in cigarette smoke, this doesn鈥檛 make them a healthy option. The e-liquid found in e-cigarettes still contains highly addictive nicotine that also increases your risk of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nicotine also increases the risk of addiction to other drugs and may impair brain development. Rather than rely on the perceived benefits of e-cigarettes, people should avoid smoking altogether.
New blood test for colon cancer screening: Questions remain
In April, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved a new screening test for colon cancer, making it the first blood-based test for this type of cancer. While this test does make it more convenient for people to get screened for colon cancer, it is also less exact than the current screening methods. It is important to discuss your risk factors and screening options with your doctor.
Does regular exercise reduce cancer risk?
It appears people with the highest levels of physical activity have lower rates of cancer of the esophagus, lung, kidney, colon, head and neck, rectum, bladder and breast, compared with people with the lowest levels of physical activity.
What is a synthetic human genome?
A group of scientists wants to develop technology to create a synthetic human genome, which could lead to improved organ transplantation, vaccines and medicines, and to new ways to fight cancer and infections.
More evidence that a healthy lifestyle might help prevent cancer
It appears that four healthy habits—getting 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, maintaining a body mass index between 18.5 and 27.5, no smoking, and drinking only in moderation—may prevent many cancer cases and death in white people.
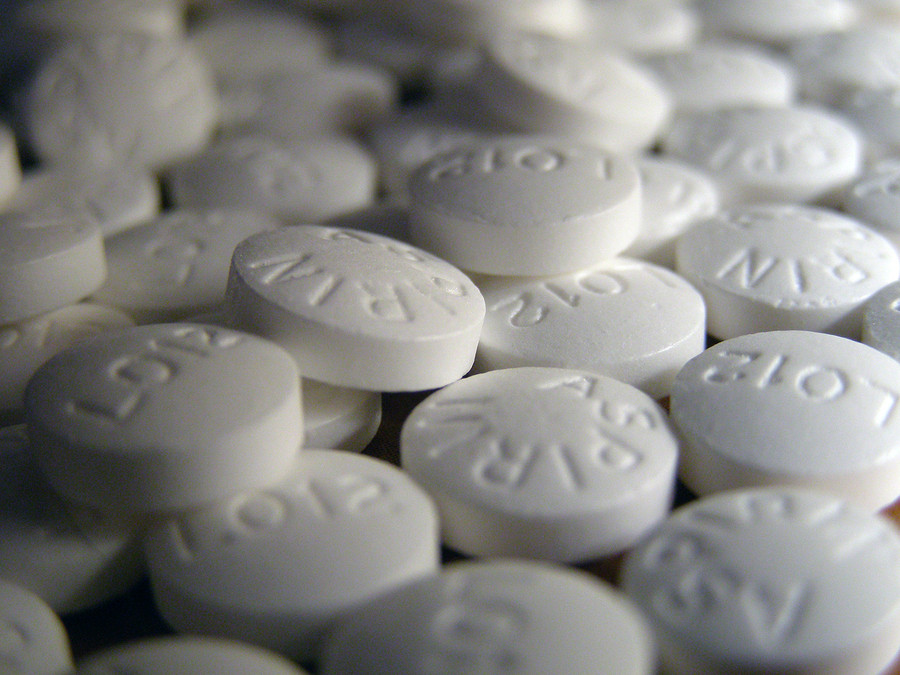
Harvard study links aspirin therapy and cancer prevention
News Briefs
Image: DimaSobko/Thinkstock
A Harvard study published March 3, 2016, in JAMA Oncology adds to increasing evidence that aspirin use may help stave off colorectal cancer and suggests that aspirin is also associated with a small reduction of overall cancer risk.
Researchers looked at aspirin use among almost 136,000 men and women in two studies over 32 years. They noted that regular aspirin use鈥攖aking either a 325-mg tablet or an 81-mg tablet two or more times per week鈥攚as associated with a 3% reduction in cancers over all, although they saw no effect on major cancers like those of the breast, prostate, or lung. The researchers say the overall reduction was due mostly to a 15% risk reduction for gastrointestinal cancer and a 19% risk reduction for colorectal cancer.
The risks of active surveillance for men with intermediate-risk prostate cancers
Many men with prostate cancer benefit from active surveillance, in which treatment doesn’t begin unless the cancer spreads. There has been some debate about whether this strategy is safe for men with intermediate-risk prostate cancer. A new study suggests that this type of cancer is more likely to spread than previously thought 鈥� but active surveillance can still be a good option for many intermediate-risk men.
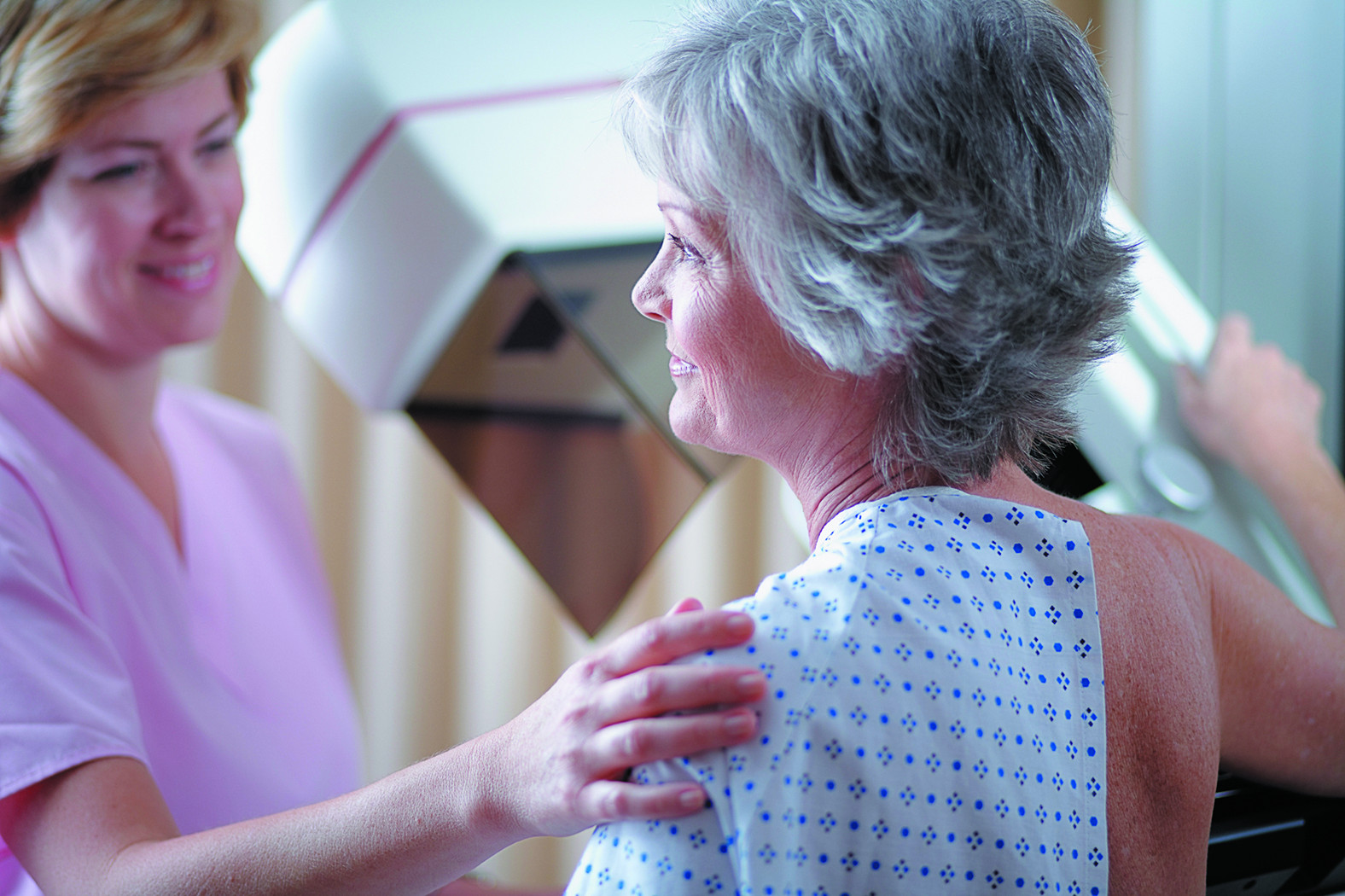
Do you really need that cancer screening?
Image: Thinkstock
A research letter published online Jan. 21, 2016, in JAMA Oncology suggests that many older adults are getting unnecessary cancer screenings. Researchers looked at questionnaire answers from about 150,000 seniors (ages 65 or older) across the country, and found that about half had received prostate-specific antigen (PSA) testing or mammography in the past year. But a third of those screened did not have a 10-year life expectancy, a major guideline for screening. Unnecessary screening rates varied by state鈥攆or example, 11% in Colorado and about 20% in Georgia. "Undergoing a screening test may actually cause more harm than good, especially with older patients or those with significant medical conditions," says Dr. Marc Garnick, an oncologist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and editor in chief of Harvard's Annual Report on Prostate Diseases. So talk to your doctor about the guidelines. Both the American Cancer Society (ACS) and the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommend routine mammograms every two years for women ages聽55 to 74. The ACS does not recommend mammograms in this age group if a woman has a life expectancy of less than 10 years.
For all men, the USPSTF recommends against routine PSA testing. The ACS suggests that men 50 or older (at average risk for prostate cancer) make the decision about screening with their doctor, but only if they have a life expectancy of at least 10 years, and only if they have been advised about the uncertainties, risks, and potential benefits of prostate cancer screening.

Tips to leverage neuroplasticity to maintain cognitive fitness as you age

Can white noise really help you sleep better?

Celiac disease: Exploring four myths

What is prostatitis and how is it treated?

What is Cushing syndrome?

Exercises to relieve joint pain

Think your child has ADHD? What your pediatrician can do

Foam roller: Could you benefit from this massage tool?

Stepping up activity if winter slowed you down

Common causes of cloudy urine
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up